GreenBSN
Overview
We are currently experiencing surging energy consumptions on the wireless cellular infrastructure. Recent reports show energy consumption of mobile networks would reach 124.4B KWh in 2011, and the power bill is expected to double in five years for one Chinese mobile operator. To build a green cellular network, we need to first improve the most critical subsystem that is the dominant contributing factor to overall energy. In the 3G context, it is the base station (BS) subsystem. BSes consume about 80% of overall infrastructure energy, while the user clients typically take around 1%. In this project, we seek to make the 3G infrastructure more energy efficient.
Research Progress
GreenBS: Traffic-Driven Power Saving in Operational 3G Cellular Networks
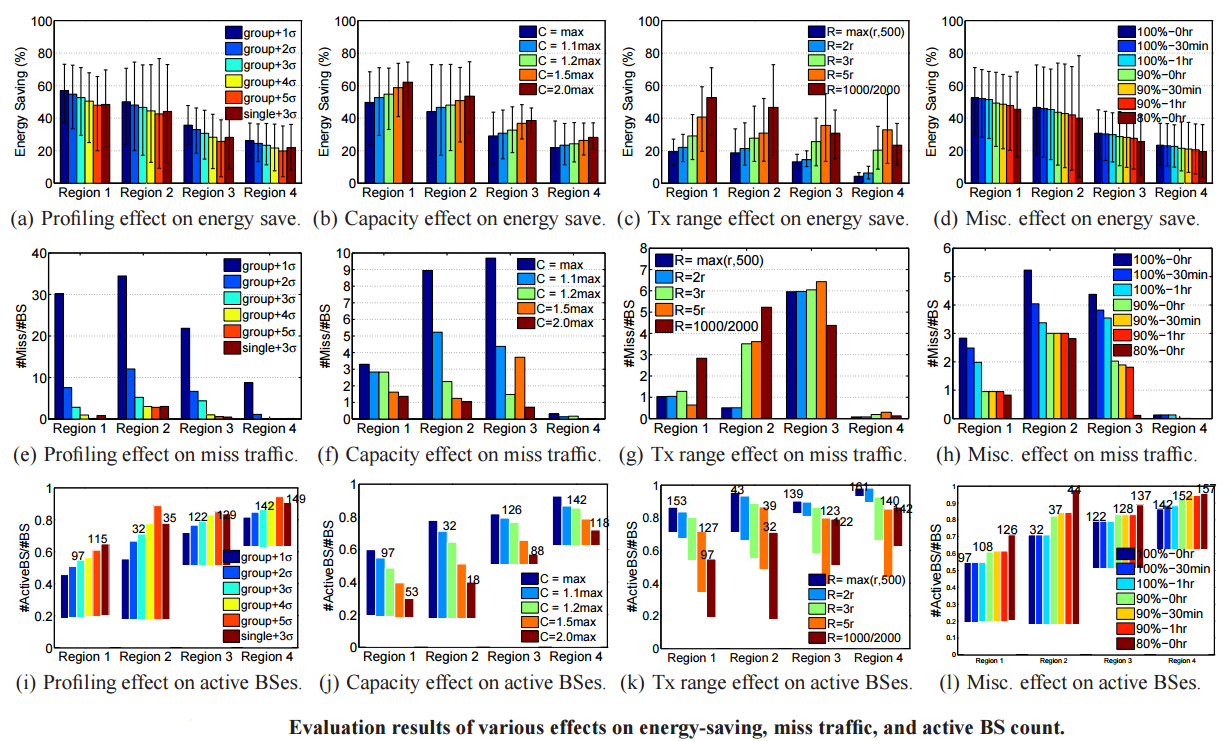
This work shows that Base stations (BSes) in the 3G cellular network are not energy proportional with respect to their carried traffic load and 3G traffic exhibits high fluctuations both in time and over space, thus incur energy waste. We proposed a profile-based approach to green cellular infrastructure. First, they profile BS traffic and approximate network-wide energy proportionality using non-load-adaptive BSes. The instrument is to leverage temporal-spatial traffic diversity and node deployment heterogeneity, and power off under-utilized BSes under light traffic. We showed that this simple scheme can yields up to a large portion of energy savings (e.g. 53% in a dense large city and 23% in a sparse, mid-sized city).
Publication
| Traffic-Driven Power Saving in Operational 3G Cellular Networks MobiCom'11 Chunyi Peng, Suk-Bok Lee, Songwu Lu, Haiyun Luo, Hewu Li |
Team Member
- Songwu Lu (University of California, Los Angeles)
- Chunyi Peng (Purdue University)
- Suk-Bok Lee (Faculty, Hanyang University, KR)
- Haiyun Luo (Director, China Mobile US Research Center)
Research Support

